Metadata and tagging
This page helps you understand metadata and add the correct values to your markdown articles (or wherever metadata are used). Metadata help readers, search engines, and AI tools find and understand your content. On Experience League, metadata helps readers filter search results by product, role, and content type (and more).
Example metadata

Certain metadata values display on published pages. For example, when you add feature, role, and level tags, they display in the TOPIC and CREATED FOR areas on Experience League.

For SEO, title and description metadata are useful to help search engines find your pages and present them to customers. They have unique editorial guidelines to follow.
The following sections can answer questions, show you what values to add, and define each value.
Frequently asked questions important
| table 0-row-2 1-row-2 2-row-2 3-row-2 4-row-2 5-row-2 6-row-2 7-row-2 8-row-2 9-row-2 | |
|---|---|
| Question | Answer |
| Is metadata required? |
Title and description must be present in an article and follow editorial requirements. However, validation fails only if description is missing or Certain metadata that might otherwise cause validation failure have fall-back defaults. For example, if title is missing, the heading 1 ( See Add metadata in Markdown to learn which values you should add to articles, TOCs, and the repo metadata files. |
| Where do I add metadata? |
Add metadata to the top of the page (see Add metadata in Markdown). You can apply values at the article (page), TOC (guide), and repo levels. Page values override values in the TOC and repository. Important: Be judicious when applying tags for |
| What values do I add first? |
A best practice is to start with title and description, then add solution, feature, topic, role, level, and so on. Technically, the order does not matter. Consider adding all your values after authoring your content, so that you deeply understand what values are best. The more you use metadata, the more you understand it. If you aren’t sure what to do, get advice from Blake, Bob, or Alva. For definitions of metadata, requirements, and examples of each tag, see the tag reference (on this page). |
| Where do I find my product’s values? | You can find them in each tag’s respective yaml file. SCCM maintains those pages. |
| How do I create or change values? |
Change or create tags by filing a Jira ticket. Use UGP as the JIRA task, and select Content Tagging as the Component. |
| How to I author Title and Description (SEO) metadata? |
Title and description have important editorial guidelines and length and case requirements that differ from an article’s H1 (page name) and first paragraph. Example title (concept): Segmentation in Analytics (title case) Example description (concept): Learn about processing options in Analytics. Get familiar with setting up rules for segmentation. Example title (task/procedure): Create a Segment Example description (task/procedure): Learn how to create a segment in Analysis Workspace. Build segments from scratch or add an existing one. |
| Where does the pipe and application name (in a Google search) come from? |
Generated automatically from metadata. Do not add the pipe and application name in title metadata. However, you can use the application name in the description. The app name is pulled from solution metadata value in the metadata.md file. |
| Where does ExL get values for Topics and Created for? |
Topics displays values from feature metadata at the top of the ExL UI. One or two feature values should exist per article. Created for displays values from role and level metadata.
|
| How is exl-id generated? | exl-id is automatically added and must be unique. When creating a page, do not use the exl-id metadata from an existing page that you plan to keep. This value must be unique on every page (and is automatically assigned). |
Add metadata in Markdown add-metadata
Add metadata at the top of each page. Order is not critical, but the best practice is to place title and description first.
The following sections describe which values belong in respective file types.
Article metadata required-article
For typical articles (and video tutorials), add the following important metadata:
- title (title case, 60 characters max.)
- description (required, cannot be blank or
null, 150 - 160 characters.)
Begin with Learn how to… (for task pages) or Learn about… (for conceptual pages) (Learn more) - Depending on content, add feature, feature-set (from the feature yaml), role, level, topic, and so on (see the tag reference section for a complete listing)
Other metadata frequently used in articles:
- If you need a shortened description for an ExL landing page, add short-description. The same editorial guidelines apply to all description metadata.
- If you need to override higher values like mini-toc-levels and solution, you can add them to an article.
- For tutorial-specific metadata, see the Technical Marketing section for recommendations.
- All other values unless explicitly set aside for a TOC or metadata file can exist in articles.
| note note |
|---|
| NOTE |
| Validation does not fail if feature, role, level, or topic are missing. For example, level is primarily used only in video tutorials, so level can be left out of product documentation articles. |
| However, validation fails if the value is blank or if a value does not match its yaml syntax values. |
| Do not use empty placeholder tags like feature with no value. |
| If you need changes or additions to the yaml lists, create a UGP JIRA task, and select Content Tagging as the Component. |
TOC metadata (guide-level) toc-metadata
TOC metadata applies to your entire guide. For example, feature-set (the parent application of a feature) and role (like Admin) are usually TOC metadata.
Do not add article metadata like feature to the TOC, unless your entire guide applies to one feature (which is rare). (If that were the case, you would add feature-set at the repo-level to validate correctly.)
Open the TOC.md and add the following metadata:
- user-guide-title - displays in the breadcrumb
- breadcrumb-title (optional, for when the user-guide-title is too long)
- user-guide-description - displays on ExL landings
- feature-set if applicable at the guide (TOC) level.
Other values you might use:
- role - for example, you might add
role: Developerto apply to all articles in the guide. If you want to override that value at the article level, you could addrole: Admin, Developerto an article.
Repo metadata (metadata.md) repo-metadata
Although not required for validation, these metadata values belong in the metadata.md file:
- git-repo - the repo URL
- solution - the application name
- type - the guide type (Documentation, Tutorial)
- cloud - the cloud name
- index - excludes the page from external search
- feature-set if applicable at the repo level.
Examples of typical repo-level metadata:
- cloud:
Experience Cloud - solution:
Experience Manager, Experience Manager Assets - type:
Tutorial - product:
adobe experience manager - role:
Business User, Admin, Developer - user-guide-title:
Experience Manager 6.5 Assets Guide
| note important |
|---|
| IMPORTANT |
Be careful when applying the same metadata fields in both the metadata.md file and TOC.md file. Values in TOC.md overwrite values in metadata.md. For example, if you set index: no in both places and then change it to index: yes in the metadata.md file, no change occurs because no is the value in the TOC. |
Metadata and tag reference tag-reference
The following is an alphabetical list of metadata tags with examples, requirements, status (current or planned use), and so on.
(If you’re new to metadata, you might want to stop and get familiar with the basics.)
auto-video-transcripts auto-video-transcripts
(Intended for -learn video tutorial repos.) Add auto-video-transcripts: true in the TOC.md or metadata.md file to enable transcripts in all videos in the guide or repo by default. You can still turn off transcripts for any individual video in the guide or repo.
See Adding video transcripts in the syntax guide for more information about adding video transcripts.
breadcrumb-title breadcrumb-title
Where used: TOC
A short title for the guide name (not an article name) that is used in the breadcrumb. Do not use in individual articles.
Example: breadcrumb-title: Components Guide
cloud cloud
Where used: Repo
For ExL search and filtering APIs. Cloud values must be title case and use spaces, where applicable. You can add multiple values by using comma separators.
Example: cloud: Document Cloud, Document Cloud
Requirements: Case sensitive and match values in cloud yaml
Log a UGP JIRA ticket with component Content Tagging if you want to add cloud values.
description description
Where used: article
Used by search engines and recommendations. Displays under the title metadata on a search engine results page. Validation fails if description does not exist (cannot be null).
Example: Learn about configuring segmentation in Analytics. Discover ways to focus on subsets of your data.
Requirements: Required for validation. Max 160 characters. See description for guidance.
If your description text included reserved syntax characters such as a second comma (example: description: Rules: Behavior and more) or a character like [ that appears immediately after the comma, validation will fail. To avoid failure, wrap the description value in quotation marks. Example: description: "Rules: Behavior and more"
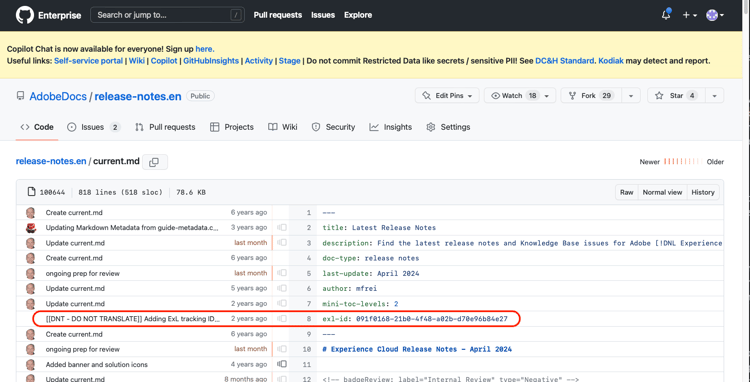
exl-id exl-id
Where used: article - an automatic, numeric ID that associates a source markdown file with a URL.
The exl-id metadata is a read-only, system-generated string added automatically to all articles.
exl-id allows us to track a published article’s source file based on a permanent ID instead of a URL that might change. These IDs are especially important currently for tutorial content in -learn repos to prevent course tracking from breaking when a URL changes after moving a file in a course repo. In the future, we hope to use exl-id values for auto-redirects.
What to do with the exl-id when copying or moving files:
When a new article is created, the system assigns an exl-id to the article and tracks it. If a writer accidentally deletes the exl-id, the system adds it back. Sometimes a writer wants to copy a file, and sometimes a writer wants to move a file. The system doesn’t know the writer’s intent.
- If you want to copy a file, delete the exl-id in the new file. If you forget to do that, a duplicate ID error occurs during validation. If you get this error, delete the exl-id in the copied file. (See tip below.)
- If you want to move the article to a different repo, remove the exl-id from the old file and add it to the copied file in the new location. Then delete the original file (and remember to add a redirect).
feature feature
Where used: article. Displays in Topics at the top of an ExL page. In a future release, users will be able to click the topic to view a list of articles tagged with that same feature. Do not use feature in the TOC file (except in the rare case where an entire guide is dedicated to a single feature).
This value is also used for ExL search, filtering APIs, and recommendations (the More help on this feature heading and bullet list added automatically at the bottom of a page).
Example: feature: Content Fragment, Processing Rules
Requirements: Match feature values within the feature-set section of the feature yaml. Feature values must be title case and use spaces, where applicable, for example, User and Groups.
You can add multiple feature values by using comma separators. When you tag your articles with appropriate feature tags, it is also necessary to specify a valid feature-set tag. The feature-set metadata is usually the same as the solution value.
Log a UGP JIRA ticket with component Content Tagging if you need to add feature values. Case sensitive.
feature-set feature-set
Where used: article, TOC.md, and metadata.md
For validation of the feature tag’s product. Sometimes, different products can use different terms (such as Reports and Reporting), so we need to validate feature values from a specific section.
Example: feature-set: Experience Manager, Experience Manager Assets
Requirements: Match values in the feature yaml. You can include multiple feature-set values.
git-repo git-repo
Where used: repo
The git-repo URL lets customers click Edit this page icon (


Example: git-repo: https://github.com/AdobeDocs/analytics.en
Requirements: If the git-repo metadata is not added, the feedback icons are not displayed in the right nav.
hide hide
Where used: article
Using ‘y’ or ‘yes’ excludes the pages from both external and internal search and the recommendations catalog. (When hide = yes, index is set to no automatically in the output file.) The article appears in the TOC unless you set hidefromtoc to yes.
If you add hide: yes to the TOC.md file, the entire guide is excluded from external and internal search and available only through a URL.
Example: hide: yes
Default is no.
See Hiding files for more information.
hidefromtoc hidefromtoc
Where used: article
If you set hidefromtoc to yes, the article does not appear in the TOC and is available only through direct links or URLs.
If all articles in a TOC section are hidden from the TOC, the section is hidden in the left nav.
Example: hidefromtoc: yes
See Hiding files for more information.
index index
Where used: article
Using n or no excludes the page from external search (if available) and from the sitemap. This value is important for pages like Contact us, soft-launches, deprecated articles, or later articles in a tutorial series.
To exclude pages from both external and internal searches, use hide.
Example: index: y
Default is no.
industries industries
Not currently in use.
interests interest
Not currently in use.
internal internal
Where used: article
Used for internal documentation for Adobe eyes only. If internal is set to yes, content is not flagged for using internal links such as git.corp.adobe.com.
Example: internal: yes
keywords keywords
Not used and not recommended. Google ignores them, and might even penalize pages with “stuffed keywords.” Coveo (internal search) also ignores keywords.
label label
Not currently in use.
landing-page-description
level level
Where used: article
Displays in Created for at the top of ExL pages. To be used for ExL search and filtering APIs. Primarily used for learning videos and courses, but also can apply to any article that has an associated product experience level recommendation.
If level (and role) do not exist, ExL does not display Created for at the top of the page.

Example: level: Experienced
Where used: article
You can add multiple level values by using comma separators such as level: Beginner, Intermediate.

Requirements: Use only a defined enum value. These values are case-sensitive - level values start with a capital letter. See the level yaml for allowed valid ENUM values.
If level metadata is not specified, the value defaults to level: Beginner
mini-toc-levels mini-toc-levels
Where used: article
This metadata determines the number of heading levels that appear in the mini-TOC in the right navigation. This metadata is usually added to the metadata.md or TOC.md file, but it’s sometimes added to individual articles.
Example: mini-toc-levels: 2
Default is 2. Valid values include 1-6.
product product
Where used: article
Used by Experience League for site analytics.
product tag is not used for search filtering. Instead, use the solution metadata for this purpose.Example: product: target
Requirements: See the product yaml for valid ENUM values.
You can only use one product tag. Multiple tags are not allowed.

Example of analytics enabled by this tag:

recommendations (“More help on this feature” widget) recommendations
Where used: article
The recommendations metadata applies to the “More help on this feature” heading and bullet list that is added automatically at the bottom of a page. It is also used to drive the content of the tiles on the “Your Personalized Home” when you sign into Experience League.
You can use noDisplay to prevent content recommendations from displaying on the page or noCatalog to exclude the page from the recommendations catalog (so it won’t be recommended).
Example: recommendations: noDisplay, noCatalog
Requirements:
noDisplayprevents recommendations from displaying on the page (can be overridden withdisplay)noCatalogexcludes the page from the catalog (can be overridden withcatalog)
More examples:
On a multi-page tutorial, you might want to set recommendations: noDisplay, noCatalog in the TOC so that users aren’t distracted while going through the tutorial and so pages in the middle of the tutorial aren’t recommended. However, to drive traffic to the first page of the tutorial, you could override the metadata on the first page with recommendations: noDisplay, catalog.
role role
Where used: article
Displays as Created for at the top of ExL pages. Used for EXL search and filtering APIs and recommendations. Primarily used for learning courses. Use only a defined enum value.
If role (and level) does not exist, ExL does not display Created for at the top of the page.
Example: role: Leader
Requirements: The four implemented roles are User, Developer, Leader, and Admin. Architect, Data Architect, and Data Engineer are valid values that are mapped to Developer. See the role yaml for valid ENUM values.
You can add multiple role values by using comma separators such as role: Developer, Data Architect.
short-description short-description
Where used: article
Optional. Used as description text on Experience League landing pages if the description is too long. This metadata was previously called “landing-page-description”.
Example: short-description: Learn how to implement tagging services for Experience Platform.
Requirements: We recommend you limit the short-description value to one sentence with no more than 20 words so that the description uses three or fewer lines on landing pages. If short-description does not exist, the description value is used.
solution solution
Where used: article
Used for ExL search filtering and recommendations. This tag differs from product, which is for site analytics.
solution and product tags are used for separate purposes, and each requires different ENUM values in their yaml files. (solution is for search filtering and product for ExL site analytics.)
Example: solution: Campaign, Campaign v8
Requirements: Must match value in solution yaml values. Multiple values allowed. Case sensitive. Fails validation when blank or incorrect values are used.
More examples:
Single solution
solution: Customer Journey Analytics
Sub-solutions (AEM and Campaign only)
solution: Experience Manager, Experience Manager Sitessolution: Campaign, Campaign Standard v7
Multiple solutions
solution: Target, Analytics, Audience Manager

For solutions that include multiple versions, such as Experience Manager and Campaign, specify multiple values. Start with the more general term (such as Campaign), and then add more specific versions (such as Campaign Standard v7).
Examples:
solution: Campaign, Campaign Standard v7solution: Experience Manager, Experience Manager Sites
Experience Platform or Data Collection.Adding or changing solution values add-or-change-solution-values
If you need a new solution value, log a JIRA issue (UGP project assigned to Bob).
If you need to replace a solution value that appears in the EXL UI, make sure that you give us at least two weeks advance notice, if possible. Log a JIRA issue (UGP project assigned to Bob). Include the deprecated value and the new value.
topic topic
Where used: article
In progress, to be used for EXL search and filtering APIs and recommendations. The topic tag is used for cross-product topics such as Integrations and Administration. Use only a defined enum value.
Example: topic: Integrations
Requirements: Topic values must be title case and use spaces, where applicable. You can add multiple topic values by using comma separators.
See the topic yaml for valid values. File a UGP JIRA ticket with Content Tagging component to add values.
title title
Where used: article
Title is for internet SEO, particularly for Google. A pipe with the product name is appended automatically.
Requirements: Required in articles. 60 characters. Sentence case. The H1 is used when this value is not present. Title differs from the page’s heading and should be written with search results in mind.
Example: Create Calculated Metrics
(Note the capitalization exception. Title metadata uses title case for capitalization.)
If your title text included reserved syntax characters such as a second comma (example: title: Rules: Behavior and more) or a character like [ that appears immediately after the comma, validation will fail. To avoid failure, wrap the title value in quotation marks. Example: title: "Rules: Behavior and more"
See Title and description for SEO for important authoring guidelines.
type type
Where used: metadata (repo) typically, and any article
Allows customers to filter by guide type and also used by recommendations.
Example: type: Tutorial
Requirements: One value only. Must match values in the type yaml. If type metadata is not specified, the value defaults to type: Documentation

type: Troubleshooting. This issue (UGP-7908) has been resolved. Non-KCS content tagged as Troubleshooting now has a left nav.version version
Example: version: 6.4
Where used: article
This is now a search filter for AEM and Campaign. Must match values in the version yaml. If a version value is specified, the accompanying solution value must also be specified. For example, you cannot use version: 6.4 if Experience Manager is not also specified as one of the solution values.
Example: version: 6.5
Possible use for EXL search and filtering APIs. Currently, multiple solution values are used for subordination.
Case sensitive. Match values in version yaml. |
user-guide-description user-guide-desc
Where used: TOC
When Experience League landing pages are generated, the user-guide-description text is pulled from the TOC.md file and displayed as the guide’s description.
When user-guide-description is missing, the description on the ExL landing is blank.
Example: user-guide-description: Learn how to administer users and products for Identity Services.
Requirements: We recommend you limit the user-guide-description value to one sentence with no more than 20 words so that the description uses 3 or fewer lines on landing pages.
(Articles use short-descrpition for ExL landing pages.)
user-guide-title user-guide-title
Where used: TOC
In limbo. Displays on ExL landings as the guide’s title.
Example: user-guide-title: Identity Services Admin Guide
Requirements: We recommend that the user-guide-title use the same text as the page title (such as # Identity Services Admin Guide {#admin}).
landing-page-name landing-page-name
Where used: metadata.md or TOC.md
Example: landing-page-name: experience-manager
Requirements: Use landing-page-name to link to the landing page to be used in the breadcrumb. Also specify landing-page-breadcrumb-title to indicate the name of the breadcrumb that appears.
landing-page-breadcrumb-title landing-page-breadcrumb-title
Where used: metadata.md or TOC.md
Example: landing-page-breadcrumb-title: AEM
Requirements: Specify landing-page-breadcrumb-title to indicate the name of the breadcrumb that appears. Also use landing-page-name to link to the landing page to be used in the breadcrumb.
last-substantial-update last-substantial-update
Where used: article
Used to indicate a major change to a page which warrants surfacing the content in “What’s new” widgets and similar functionality, because system-generated timestamps update on any minor markdown change.
Example: last-substantial-update: 2025-12-31
Technical Marketing metadata metadata-desc
The following metadata are specific to the Technical Marketing team.
doc-typeactivitysub-productExample: sub-product: search
You can use sub-product for Adobe Analytics (Omega) data, among other applications. The sub-product values are less restrictive than product values. Work with solution teams to determine enum values for sub-products in your solution.
Example: livefyre could include library, search, instagram-search, apps, media-wall, carousel. Experience Manager could include assets, sites, community and so on.
ktUsed by Technical Marketing team.
Example: kt: <jira-number>
Last Updatedlast-substantial-updateteamteam: TMthumbnailtitle displays in Google, and a pipe with the product name is appended automatically. See Title and description for SEO for authoring guidelines.Landing Page Metadata (EXL)
Landing Page Metadata is EXL only. We use metadata in landing pages to define the breadcrumb experience.
Breadcrumb format:
Home > [Solution] > [Guide Name] > [article-name].html
Home jumps to the main AdobeDocs landing page. Likely https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/home.html
Solution jumps to the solution landing page, such as Analytics or Experience Platform.
Guide Name jumps to the home page of the user guide.
The article name is not a link.
child-repos (legacy) child-repos
child-repos: id-service, core-services, core-services-learn, device-coop
The child-repos tag in the landing pages is being replace in v2 by landing-page-name and landing-page-breadcrumb-title in the repo itself. Refer to those options.
For v1, add the repo names (no language suffix) to the child-repos metadata on the landing page. Any content within a child repo uses the breadcrumb information from the landing page in which the child-repo is specified. For example, if id-service is added as a child repo to Core Services, any ID Service article has this breadcrumb:
Home > Core Services > ID Service User Guide > article name
A repo can be added as a child repo to only one landing page (although the repo can be linked to from multiple repos).
parent-landing-page parent-landing-page
parent-landing-page: experience-manager-landing.md
This is used for special tutorials landing pages (or possibly sub-landing pages) to make sure that the appropriate landing page appears in the breadcrumb.
Requesting new metadata values create-metadata
If you need changes or additions to the yaml lists, create a UGP JIRA task, and select Content Tagging as the Component.
Uploading metadata from a CSV file (Admin)
Uploading metadata from a CSV file can be a great time saver. It’s especially useful for updating title and description metadata and for assigning feature metadata to articles.
Contact Bob if you want to run this workflow either on your own or with help.
-
(Writers) develop a list of values for the metadata yaml files (feature, solution, role, and so on).
To add values to any yaml file, create a UGP JIRA task, and select Content Tagging as the Component.
-
(Writers) Make sure that your repo is up to date. Remove any previous
__metadata_updatesbranch andguide-metadata.csvfile or files. -
(Bob) Run the batch job or the individual generateMetaCsvFiles Jenkins job.
Specify the metadata to be included. Default: title, description, feature, topic, role, level.
This job creates a branch called
__metadata_updatesand uploads a separateguide-metadata.csvfile in the same directory as its corresponding TOC.md file. -
(Writer) Switch to the
__metadata_updatesbranch and edit theguide-metadata.csvfiles. When you’re done, tell Bob that you’re ready to upload.
-
(Bob) Add
feature-setvalue tometadata.mdor individualTOC.mdfiles. -
(Bob) Run the updateMetaFromCsvFiles Jenkins job to upload the metadata from the CSV to the individual files.
-
(Bob) Remove the CSV files from the branch and submit a PR.
-
(Bob) Let writer know when complete.
Metadata not in Use
uuid
Some files include uuid values from migration. If your content has already been migrated and redirects from the preview authoring system are in place, you can delete these uuid values.
audience
Example: audience: administrator
Not in use. Instead, use role (see above).
difficulty
Not in use. Instead, use level (see above).
badge
Example: badge: premium
We used this term during migration for Target to flag premium content so we could add a “Premium” badge image to the title. This metadata is used only for reference currently.
If you want a badge for your solution, contact the SSE team.
author
Example: author: John Doe
Not yet used.
last-updated
Example: last-updated: n
Default is yes. If you change the metadata to “last-updated: n”—-such as for minor changes—-the “Last updated” date in the right rail will not be updated. Not yet implemented.
private-beta
Example: private-beta: y
Not yet in use. Default is no.
private-feature-pack
Example: private-feature-pack: y
Not yet in use. For AEM, we might use Private Feature Pack and Admitted Domains from helpx. Default is no. If you select this option, admitted-domains is also required. We should verify admitted-domains is specified if private is enabled. Does not allow publish if not specified.
admitted-domains
Example: admitted-domains: <string>
Not yet in use. Required for AEM private feature packs.
legacypath
For AEM
internal
Example: internal: y
For KB docs. Default is no. Way to publish content for Adobe tech support operators only. Not yet in use.
Previous and Next buttons
The Previous and Next buttons that appear at the bottom of the page are not configured through article metadata. Instead, Previous/Next button functionality is managed via repo configuration. There are three options:
- Full (default) - Previous/Next buttons appear at the bottom of every article.
- Sibling only - Previous/Next buttons appear at the bottom of every article preceded and followed by an article on the same TOC level, but the Previous button is absent if there’s no preceding sibling article, and the Next button is absent if there’s no subsequent sibling article.
- Off - Previous/Next buttons are turned off for all guides and articles in the repo.
To change how Previous/Next buttons work, submit a JIRA ticket assigned to Bob.
original-author
last-author
original-publish
Deprecated Metadata
seo-title
No longer used. The title metadata is used for SEO. The H1 (#) title is used for page display.
seo-description
No longer used. The description metadata is used for SEO. For any page display of description, use different supported metadata such as short-description or user-guide-description.
solution-title
Example: solution-title: Learn & Support
Required for AEM. Not used for EXL. This item is the link text for the first of three links in the header. For standard help guides, use “Learn & Support” unless you need to create a link to different content.
solution-hub-url
Example: solution-hub-url: https://helpx.adobe.com/support/analytics.html
Required for AEM. Not used for EXL. The hub URL determines the link destination when users click the Product name in the user guide header.
solution-icon
Example: solution-icon: assets/logo-24.png
Never used. Intended to be used for solution icon in the header.
getting-started-title
Example: getting-started-title: Getting Started
Required for AEM. Not used for EXL. This item is the link text for the second of three links in the header. Use “Getting Started” unless you need to create a link to different content.
getting-started-url
Example: getting-started-url: https://landing.adobe.com/experience-league/
Required for AEM. Not used for EXL. The getting started URL determines the link destination when users click the middle link in the header.
tutorials-title
Example: tutorials-title: Tutorials
Required for AEM. Not used for EXL. This item is the link text for the third of three links in the header. Use “Tutorials” unless you need to create a link to different content.
tutorials-url
tutorials-url: https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-cloud/tutorials.html
Required for AEM. Not used for EXL. The tutorials URL determines the link destination when users click the third link in the header.
user-guide-url
Example: user-guide-url: /content/help/en/audience-manager/user-guide/aam-home.html
Never used. Ignore or delete.
Metadata log files for reference
Open any CSV file in a spreadsheet to see all the metadata in each file in the repo.
- adobe-consulting-services.en
- adobe-developers-live-events.en
- adobe-system-status.en
- advertising-cloud-learn.en
- advertising-cloud.en
- aem-forms-automated-conversion-service.en
- aem-guides-wknd-assets-docs.en
- analytics-learn.en
- analytics-platform.en
- analytics.en
- asset-compute.en
- audience-manager-admin.en
- audience-manager-learn.en
- audience-manager.en
- auditor.en
- authoring-guide-exl.en
- bizible.en
- blueprints-learn.en
- campaign-classic-learn.en
- campaign-classic.en
- campaign-learn.en
- campaign-standard-learn.en
- campaign-standard.en
- campaign.en
- contextualhelptest.en
- contributor.en
- control-panel.en
- core-services.en
- creative-cloud-enterprise-learn.en
- creative-cloud-enterprise.en
- customer-care-office-hours.en
- customer-journey-analytics-learn.en
- customer-journey-management.en
- customer-one.en
- cxm-learn.en
- data-workbench.en
- debugger-learn.en
- debugger.en
- deliverability-learn.en
- destination-sdk.en
- device-co-op.en
- document-cloud-enterprise.en
- document-cloud-learn.en
- document-cloud-mobile.en
- document-cloud-sign.en
- document-services.en
- dynamic-media-classic.en
- dynamic-media-developer-resources.en
- experience-cloud-kcs.en
- experience-cloud.en
- experience-manager-64.en
- experience-manager-65.en
- experience-manager-assets-essentials.en
- experience-manager-brand-portal.en
- experience-manager-cloud-manager.en
- experience-manager-cloud-service.en
- experience-manager-core-components.en
- experience-manager-desktop-app.en
- experience-manager-dispatcher.en
- experience-manager-document-security.en
- experience-manager-forms-cloud-service.en
- experience-manager-gems.en
- experience-manager-htl.en
- experience-manager-learn.en
- experience-manager-pattern-detection.en
- experience-manager-release-information.en
- experience-manager-screens.en
- experience-manager-skill-builder.en
- experience-platform.en
- id-service.en
- journey-optimizer-learn.en
- journey-optimizer.en
- journey-orchestration-learn.en
- journeys.en
- kcs-dev.en
- landing-pages.en
- launch-learn.en
- launch.en
- livefyre.en
- magento-learn.en
- magento-paas.en
- marketo.en
- media-analytics.en
- mobile-sdk-learn.en
- mobile-services.en
- offer-decisioning-learn.en
- offer-decisioning.en
- partner-exchange.en
- places.en
- platform-learn.en
- primetime.en
- release-notes.en
- search-promote.en
- skill-builder-events.en
- skill-exchange-events.en
- target-learn.en
- target.en
- web-sdk-learn.en
