Expression editor overview expression
Editing an expression involves manually entering conditions to form a rule. This mode allows you to use advanced functions, which let you manipulate the values used to carry out specific queries such as manipulating dates, strings, numerical fields, sorting, etc.
Work with the expression editor edit
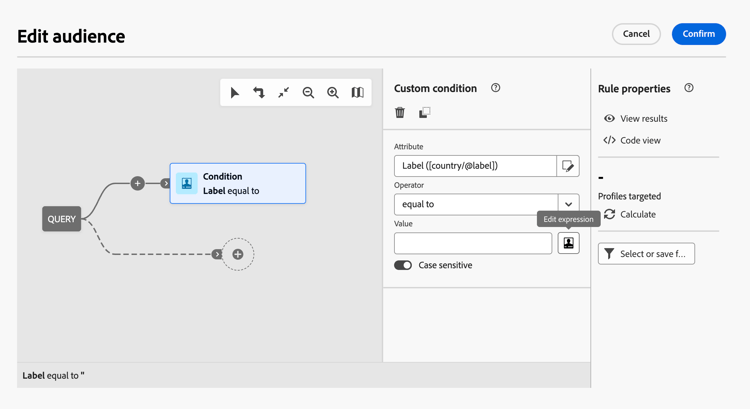
The expression editor is available from the query modeler Edit expression button, available for the Attribute and Value fields when configuring a custom condition.
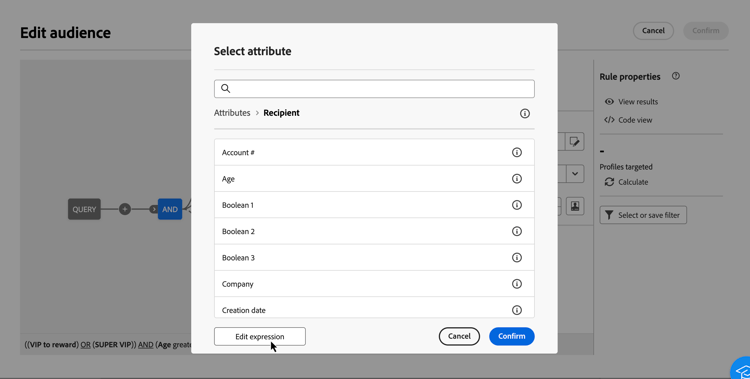
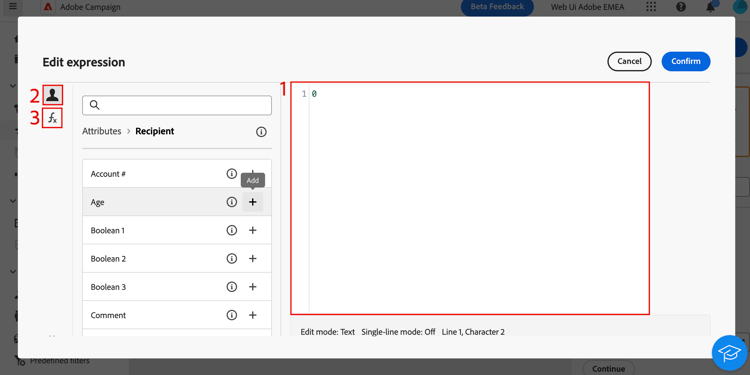
The expression editor provides:
- An input field (1) in which the expression is defined.
- The list of available fields (2) that can be used in the expression and corresponding to the schema, also known as targeting dimension, of the query.
- Helper functions (3), sorted by category.
Edit the expression by entering an expression directly in the input field. To add a field or a helper function, place your cursor in the expression where you want to add it and select the + button.
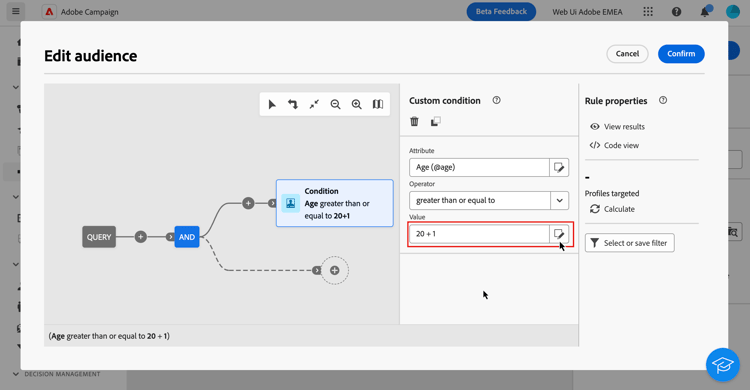
When your expression is ready, select Confirm. The expression displays in the selected field. To edit it, open the expression editor and make the desired changes.
The example below shows an expression configured for the Value field. To edit it, you need to open the expression editor using the Edit expression button.
Helper functions
The query editing tool allows you to use advanced functions to carry out complex filtering depending on the desired results and the types of manipulated data. The following functions are available:
Date
The date functions are used to manipulate date or time values.
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 5-row-4 6-row-4 7-row-4 8-row-4 9-row-4 10-row-4 11-row-4 12-row-4 13-row-4 14-row-4 15-row-4 16-row-4 17-row-4 18-row-4 19-row-4 20-row-4 21-row-4 22-row-4 23-row-4 24-row-4 25-row-4 26-row-4 27-row-4 28-row-4 29-row-4 30-row-4 31-row-4 32-row-4 33-row-4 34-row-4 35-row-4 36-row-4 37-row-4 38-row-4 39-row-4 40-row-4 41-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| AddYears | Adds the specified number of years to the provided datetime. | AddYears(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddYears(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 3) |
| AddMonths | Adds the specified number of months to the provided datetime. | AddMonths(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddMonths(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 6) |
| AddDays | Adds the specified number of days to the provided datetime. | AddDays(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddDays(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 10) |
| AddHours | Adds the specified number of hours to the provided datetime. | AddHours(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddHours(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 3) |
| AddMinutes | Adds the specified number of minutes to the provided datetime. | AddMinutes(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddMinutes(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 32) |
| AddSeconds | Adds the specified number of seconds to the provided datetime. | AddSeconds(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddSeconds(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 37) |
| SubYears | Subtracts the specified number of years to the provided datetime. | SubYears(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubYears(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 3) |
| SubMonths | Subtracts the specified number of months to the provided datetime. | SubMonths(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubMonths(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 6) |
| SubDays | Subtracts the specified number of days to the provided datetime. | SubDays(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubDays(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 10) |
| SubHours | Subtracts the specified number of hours to the provided datetime. | SubHours(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubHours(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 3) |
| SubMinutes | Subtracts the specified number of minutes to the provided datetime. | SubMinutes(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubMinutes(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 32) |
| SubSeconds | Subtracts the specified number of seconds to the provided datetime. | SubSeconds(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubSeconds(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 37) |
| Year | Extracts the year from the given datetime object. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Month | Extracts the month from the given datetime object. | Month(<DATETIME>) | Month(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Day | Extracts the day from the given datetime object. | Day(<DATETIME>) | Day(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| DayOfYear | Extracts the day of year from the given datetime object. For example, if the provided datetime is February 2nd, it would return 33. | DayOfYear(<DATETIME>) | DayOfYear(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| WeekDay | Extracts the day of the week from the given datetime object, as a number from 0 to 6, with 0 representing Sunday. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Hour | Extracts the hour value from the given datetime object. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Minute | Extracts the minute value from the given datetime object. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Second | Extracts the second value from the given datetime object. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| YearsDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of years. | YearsDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | YearsDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| MonthsDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of months. | MonthsDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | MonthsDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| DaysDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of days. | DaysDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | DaysDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| HoursDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of hours. | HoursDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | HoursDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| MinutesDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of minutes. | MinutesDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | MinutesDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| SecondsDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of seconds. | SecondsDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | SecondsDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| YearsOld | Finds the difference between the given datetime and the present, with a granularity of years. | YearsOld(<DATETIME>) | YearsOld(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| MonthsOld | Finds the difference between the given datetime and the present, with a granularity of months. | MonthsOld(<DATETIME>) | MonthsOld(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| DaysOld | Finds the difference between the given datetime and the present, with a granularity of days. | DaysOld(<DATETIME>) | DaysOld(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| GetDate | Get the current date of the server. | GetDate() | GetDate() |
| DateOnly | Truncates the datetime to just the year, month, and day. | DateOnly(<DATETIME>) | DateOnly(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| ToDate | Converts the field to a date field. | ToDate(<DATETIME>) | ToDate(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| ToDateTime | Converts the field to a datetime field. | ToDateTime(<DATE>) | ToDateTime(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| ToTimestamp | Converts the field to a timestamp field. | ToTimestamp(<DATETIME>) | ToTimestamp(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| Oldest | Returns the oldest date between the two provided. | Oldest(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | Oldest(“2015-02-13 11:59:59”, “2016-04-13 19:28:14”) |
| TruncDate | Truncates the datetime to the nearest unit, based on the numerical value given. If the numeric value is equal to 60, it truncates to the nearest minute. If the numeric value is equal to 3600, it truncates to the nearest hour. If the numeric value is equal to 86400, it truncates to the nearest day. Otherwise, it truncates to the nearest second. | TruncDate(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | TruncDate(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”, 3600) |
| TruncDateTZ | Truncates the datetime to the nearest unit, based on the numerical value given, and sets the datetime to the specified timezone. If the numeric value is equal to 60, it truncates to the nearest minute. If the numeric value is equal to 3600, it truncates to the nearest hour. If the numeric value is equal to 86400, it truncates to the nearest day. | TruncDateTZ(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>, <TIMEZONE>) | TruncDateTZ(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”, 3600, “America/Los_Angeles”) |
| TruncTime | Sets the datetime to January 1st, 2000 and rounds the rest of the datetime to the nearest unit, based on the numerical value given.If the numeric value is equal to 60, it truncates to the nearest minute. If the numeric value is equal to 3600, it truncates to the nearest hour. | TruncTime(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | TruncTime(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”, 3600) |
| TruncQuarter | Truncates the datetime to the first date in the nearest quarter. | TruncQuarter(<DATETIME>) | TruncQuarter(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”) |
| TruncYear | Truncates the datetime to the first date in the nearest year. | TruncYear(<DATETIME>) | TruncYear(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”) |
| TruncWeek | Truncates the datetime to the Sunday of the nearest week. | TruncWeek(<DATETIME>) | TruncWeek(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”) |
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 5-row-4 6-row-4 7-row-4 8-row-4 9-row-4 10-row-4 11-row-4 12-row-4 13-row-4 14-row-4 15-row-4 16-row-4 17-row-4 18-row-4 19-row-4 20-row-4 21-row-4 22-row-4 23-row-4 24-row-4 25-row-4 26-row-4 27-row-4 28-row-4 29-row-4 30-row-4 31-row-4 32-row-4 33-row-4 34-row-4 35-row-4 36-row-4 37-row-4 38-row-4 39-row-4 40-row-4 41-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| AddYears | Adds the specified number of years to the provided datetime. | AddYears(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddYears(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 3) |
| AddMonths | Adds the specified number of months to the provided datetime. | AddMonths(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddMonths(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 6) |
| AddDays | Adds the specified number of days to the provided datetime. | AddDays(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddDays(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 10) |
| AddHours | Adds the specified number of hours to the provided datetime. | AddHours(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddHours(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 3) |
| AddMinutes | Adds the specified number of minutes to the provided datetime. | AddMinutes(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddMinutes(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 32) |
| AddSeconds | Adds the specified number of seconds to the provided datetime. | AddSeconds(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | AddSeconds(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 37) |
| SubYears | Subtracts the specified number of years to the provided datetime. | SubYears(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubYears(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 3) |
| SubMonths | Subtracts the specified number of months to the provided datetime. | SubMonths(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubMonths(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 6) |
| SubDays | Subtracts the specified number of days to the provided datetime. | SubDays(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubDays(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 10) |
| SubHours | Subtracts the specified number of hours to the provided datetime. | SubHours(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubHours(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 3) |
| SubMinutes | Subtracts the specified number of minutes to the provided datetime. | SubMinutes(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubMinutes(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 32) |
| SubSeconds | AdSubtractsds the specified number of seconds to the provided datetime. | SubSeconds(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | SubSeconds(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, 37) |
| Year | Extracts the year from the given datetime object. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Month | Extracts the month from the given datetime object. | Month(<DATETIME>) | Month(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Day | Extracts the day from the given datetime object. | Day(<DATETIME>) | Day(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| DayOfYear | Extracts the day of year from the given datetime object. For example, if the provided datetime is February 2nd, it would return 33. | DayOfYear(<DATETIME>) | DayOfYear(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| WeekDay | Extracts the day of the week from the given datetime object, as a number from 1 to 7, with 1 representing Sunday. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Hour | Extracts the hour value from the given datetime object. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Minute | Extracts the minute value from the given datetime object. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| Second | Extracts the second value from the given datetime object. | Year(<DATETIME>) | Year(“2019-12-15 15:30:00”) |
| YearsDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of years. | YearsDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | YearsDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| MonthsDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of months. | MonthsDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | MonthsDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| DaysDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of days. | DaysDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | DaysDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| HoursDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of hours. | HoursDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | HoursDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| MinutesDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of minutes. | MinutesDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | MinutesDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| SecondsDiff | Finds the difference between the given datetimes, with a granularity of seconds. | SecondsDiff(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | SecondsDiff(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”, “2018-10-14 18:35:27”) |
| MonthsOld | Finds the difference between the given datetime and the present, with a granularity of months. | MonthsOld(<DATETIME>) | MonthsOld(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| DaysOld | Finds the difference between the given datetime and the present, with a granularity of days. | DaysOld(<DATETIME>) | DaysOld(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| GetDate | Get the current date of the server. | GetDate() | GetDate() |
| DateOnly | Truncates the datetime to just the year, month, and day. | DateOnly(<DATETIME>) | DateOnly(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| ToDate | Converts the field to a date field. | ToDate(<DATETIME>) | ToDate(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| ToDateTime | Converts the field to a datetime field. | ToDateTime(<DATE>) | ToDateTime(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| ToTimestamp | Converts the field to a timestamp field. | ToTimestamp(<DATETIME>) | ToTimestamp(“2019-12-25 15:30:00”) |
| Oldest | Returns the oldest date between the two provided. | Oldest(<DATETIME>, <DATETIME>) | Oldest(“2015-02-13 11:59:59”, “2016-04-13 19:28:14”) |
| TruncDate | Truncates the datetime to the nearest unit, based on the numerical value given. If the numeric value is equal to 60, it truncates to the nearest minute. If the numeric value is equal to 3600, it truncates to the nearest hour. If the numeric value is equal to 86400, it truncates to the nearest day. Otherwise, it truncates to the nearest second. | TruncDate(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | TruncDate(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”, 3600) |
| TruncDateTZ | Truncates the datetime to the nearest unit, based on the numerical value given, and sets the datetime to the specified timezone. If the numeric value is equal to 60, it truncates to the nearest minute. If the numeric value is equal to 3600, it truncates to the nearest hour. If the numeric value is equal to 86400, it truncates to the nearest day. | TruncDateTZ(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>, <TIMEZONE>) | TruncDateTZ(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”, 3600, “America/Los_Angeles”) |
| TruncTime | Sets the datetime to January 1st, 2000 and rounds the rest of the datetime to the nearest unit, based on the numerical value given.If the numeric value is equal to 60, it truncates to the nearest minute. If the numeric value is equal to 3600, it truncates to the nearest hour. | TruncTime(<DATETIME>, <NUMBER>) | TruncTime(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”, 3600) |
| TruncQuarter | Truncates the datetime to the first date in the nearest quarter. | TruncQuarter(<DATETIME>) | TruncQuarter(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”) |
| TruncYear | Truncates the datetime to the first date in the nearest year. | TruncYear(<DATETIME>) | TruncYear(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”) |
| TruncWeek | Truncates the datetime to the Sunday of the nearest week. | TruncWeek(<DATETIME>) | TruncWeek(“2016-04-13 19:28:14”) |
| ConvertNTZ | Converts a timestamp with no timezone to a timestamp with a timezone. The attached timezone will be the timezone of the external account. | ConvertNTZ(<DATETIME>) | ConvertNTZ(“2024-06-24 14:43:49”) |
Geomarketing
The geomarketing functions are used to manipulate geographical values.
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| Distance | Returns the distance between two points defined by their longitude and latitude in degrees, as a double. | Distance(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>, <NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | Distance(40.345, 39.2345, -35.5834, 34.599) |
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| Distance | Returns the distance between two points defined by their longitude and latitude in degrees, as a double. | Distance(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>, <NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | Distance(40.345, 39.2345, -35.5834, 34.599) |
Numeric
The numeric functions are used to convert text to numbers.
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 5-row-4 6-row-4 7-row-4 8-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| Mod | Returns the remainder of the first number divided by the second number. | Mod(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | Mod (3, 2) |
| Percent | Calculates what percentage the first number is of the second number. | Percent(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | Percent(1, 2) |
| Random | Returns a random number between 0 (inclusive) and 1 (exclusive). | Random() | Random () |
| Round | Returns the provided number to the nearest requested decimal place. | Round(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | Round(4.5394, 2) |
| ToDouble | Converts the provided number to a double. | ToDouble(<NUMBER>) | ToDouble(5) |
| ToInteger | Converts the provided number to an integer. | ToInteger(<NUMBER>) | ToInteger(45) |
| ToInt64 | Converts the provided number to a 64-bit integer. | ToInt64(<NUMBER>) | ToInt64(493) |
| Trunc | Truncates the provided number to the requested number of decimal places. | Trunc(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | Trunc(36.9348934, 3) |
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 5-row-4 6-row-4 7-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| Mod | Returns the remainder of the first number divided by the second number. | Mod(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | Mod (3, 2) |
| Percent | Calculates what percentage the first number is of the second number. | Percent(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | Percent(1, 2) |
| Random | Returns a random number between 0 (inclusive) and 1 (exclusive). | Random() | Random () |
| ToDouble | Converts the provided number to a double. | ToDouble(<NUMBER>) | ToDouble(5) |
| ToInteger | Converts the provided number to an integer. | ToInteger(<NUMBER>) | ToInteger(45) |
| ToInt64 | Converts the provided number to a 64-bit integer. | ToInt64(<NUMBER>) | ToInt64(493) |
| Trunc | Truncates the provided number to the requested number of decimal places. | Trunc(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | Trunc(36.9348934, 3) |
Others
This table contains the remaining functions available.
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 5-row-4 6-row-4 7-row-4 8-row-4 9-row-4 10-row-4 11-row-4 12-row-4 13-row-4 14-row-4 15-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| Case | Returns the first value if the expression is true. Otherwise, returns the second value. | Case(When(<EXPRESSION> <VALUE>), Else(<VALUE>)) | Case(When(a > b, “yes”), Else(“no”)) |
| When | Used as part of the Case function. Used to check the expression within Case. | When(<EXPRESSION> <VALUE>) | When(a > b, “yes”) |
| Else | Used as part of the Case function. Used to choose the other option, if the When expression is false. | Else(<VALUE>) | Else (“no”) |
| Coalesce | Returns the first non-null value. | Coalesce(<VALUE>, <VALUE>) | Coalesce (“”, “string”) |
| Decode | Returns the first option if the values are equal. Returns the second option if the values are not equal. | Decode(<VALUE>, <VALUE>, <VALUE>, <VALUE>) | Decode(1, 2, “true”, “false”) |
| GetEmailDomain | Extracts the domain from the provided email address. | GetEmailDomain(<STRING>) | GetEmailDomain(“sample@example.com”) |
| Iif | Returns the first option if the condition is true and returns the second option if the condition is false. | Iif(<CONDITION>, <VALUE>, <VALUE>) | Iif(10 < 20, “true”, “false”) |
| IsEmptyString | Returns the first option if the string is empty. Otherwise, returns the second option. | IsEmptyString( <STRING> ,<VALUE>, <VALUE>) | IsEmptyString(“string”, “yes”, “no”) |
| NewUUID | Generates a new unique UUID. | NewUUID() | NewUUID() |
| NoNull | Returns the provided string if it’s not empty, and returns an empty string if the provided string is empty. | NoNull(<STRING>) | NoNull(“test”) |
| IsBitSet | Performs a bitwise and (&) on the provided numbers. This lets you check if the bit within the first parameter is set at the position provided in the second parameter. | IsBitSet(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | IsBitSet(5, 3) |
| ClearBit | This lets your clear the bit within the first parameter at the position provided in the second parameter. | ClearBit(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | |
| SetBit | Performs a bitwise or (|) on the provided numbers. This lets you set the bit within the first parameter is set at the position provided in the second parameter. | SetBit(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | SetBit(5, 3) |
| RowId | Returns the line number. | RowId() | RowId() |
| ToBoolean | Converts the value to a boolean. | ToBoolean(<VALUE>) | ToBoolean(a=b) |
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 5-row-4 6-row-4 7-row-4 8-row-4 9-row-4 10-row-4 11-row-4 12-row-4 13-row-4 14-row-4 15-row-4 16-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| Case | Returns the first value if the expression is true. Otherwise, returns the second value. | Case(When(<EXPRESSION> <VALUE>), Else(<VALUE>)) | Case(When(a > b, “yes”), Else(“no”)) |
| When | Used as part of the Case function. Used to check the expression within Case. | When(<EXPRESSION> <VALUE>) | When(a > b, “yes”) |
| Else | Used as part of the Case function. Used to choose the other option, if the When expression is false. | Else(<VALUE>) | Else (“no”) |
| GetEmailDomain | Extracts the domain from the provided email address. | GetEmailDomain(<STRING>) | GetEmailDomain(“sample@example.com”) |
| Iif | Returns the first option if the condition is true and returns the second option if the condition is false. | Iif(<CONDITION>, <VALUE>, <VALUE>) | Iif(10 < 20, “true”, “false”) |
| IsEmptyString | Returns the first option if the string is empty. Otherwise, returns the second option. | IsEmptyString( <STRING> ,<VALUE>, <VALUE>) | IsEmptyString(“string”, “yes”, “no”) |
| ToBoolean | Returns 1 if the value is true. Returns 0 if the value is false. | ToBoolean(<VALUE>) | ToBoolean(a=b) |
| ToBooleanType | Converts the value to a boolean. | ToBooleanType(<VALUE>) | ToBooleanType(a=b) |
| IsBitSet | Performs a bitwise and (&) on the provided numbers. This lets you check if the bit within the first parameter is set at the position provided in the second parameter. | IsBitSet(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | IsBitSet(5, 3) |
| ClearBit | This lets your clear the bit within the first parameter at the position provided in the second parameter. | ClearBit(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | |
| SetBit | Performs a bitwise or (|) on the provided numbers. This lets you set the bit within the first parameter is set at the position provided in the second parameter. | SetBit(<NUMBER>, <NUMBER>) | SetBit(5, 3) |
| RowId | Returns the line number. | RowId() | RowId() |
| NewUUID | Generates a new unique UUID. | NewUUID() | NewUUID() |
| NoNull | Returns the provided string if it’s not empty, and returns an empty string if the provided string is empty. | NoNull(<STRING>) | NoNull(“test”) |
| AESEncrypt | Encrypts the provided string with the AES encryption type. | AESEncrypt() | AESEncrypt(“hello”) |
| ObjectConstruct | Creates an object based off of the provided key/value pairs. | ObjectConstruct(<STRING>, <STRING>) | ObjectConstruct(“key”, “value”) |
String
The string functions are used to manipulate a set of strings.
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 5-row-4 6-row-4 7-row-4 8-row-4 9-row-4 10-row-4 11-row-4 12-row-4 13-row-4 14-row-4 15-row-4 16-row-4 17-row-4 18-row-4 19-row-4 20-row-4 21-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| AllNonNull2 | Takes two strings and checks if all of them are not null and not empty. | AllNonNull2(<STRING>, <STRING>) | AllNonNull2(“”, “string2”) |
| AllNonNull3 | Takes three strings and checks if all of them are not null and not empty | AllNonNull3(<STRING>, <STRING>, <STRING>) | AllNonNull3(“”, “one”, “three”) |
| Ascii | Takes a string and returns the resulting . | Ascii(<STRING>) | Ascii (“foo”) |
| Char | Takes an array of Unicode codepoints and returns the resulting string. | Char(<ARRAY>) | Char([65, 68, 79, 66, 69]) |
| Charindex | Finds the first occurrence of the specified substring within the main string. | Charindex(<STRING>, <SUBSTRING>) | Charindex (“bar@example.com”, “@”) |
| dataLength | Returns the number of bytes in the string. | dataLength(<STRING>) | dataLength(“My string”) |
| GetLine | Return the requested line of the provided string. | GetLine(<STRING>, <NUMBER>) | GetLine(multilinestring, 5) |
| IfEquals | Takes four strings and returns the third string if the first two strings are equal and returns the fourth string if the first two strings are not equal. | IfEquals(<STRING>, <STRING>, <STRING>, <STRING>) | IfEquals(“a”, “a”, “yes”, “no”) |
| IsMemoNull | Returns 1 if the string is null, otherwise it returns 0. | IsMemoNull(<STRING>) | IsMemoNull(“hello”) |
| JuxtWords | Takes two strings and combines them into a single string. Spaces between the strings are added if required. | JuxtWords(<STRING>, <STRING>) | JuxtWords(“Hello”, “World”) |
| JuxtWords3 | Takes three strings and combines them into a single string. Spaces between the strings are added if required. | JuxtWords3(<STRING>, <STRING>, <STRING>) | JuxtWords3(“Hello”, “New”, “World”) |
| Left | Takes a string and returns the leftmost characters as specified. | Left(<STRING>, <NUMBER>) | Left(“Substring”, 3) |
| Length | Returns the length of the string. | Length(<STRING>) | Length(“MyString”) |
| Md5Digest | Converts the MD5-hashed string into its hexadecimal representation. | Md5Digest(<STRING>) | Md5Digest(“String”) |
| MemoContains | Checks if the string contains the provided substring. | MemoContains(<STRING>, <STRING>) | MemoContains(“string”, “str”) |
| Right | Takes a string and returns the rightmost characteres as specified. | Right(<STRING>, <NUMBER>) | Right (“Substring”, 3) |
| Smart | Returns the string with the first letter of each word capitalized. | Smart(<STRING>) | Smart(“hello world”) |
| Substring | Take a string and returns a portion of the provided string, based on the positions given. | Substring(<STRING>, <LEFT_NUMBER>, RIGHT_NUMBER>) | Substring(“Substring”, 3, 5) |
| Sha256Digest | Converts the SHA256-hashed string into its hexadecimal representation. | Sha256Digest(<STRING>) | Sha256Digest(“string”) |
| Sha512Digest | Converts the SHA512-hashed string into its hexadecimal representation. | Sha512Digest(<STRING>) | Sha512Digest(“string”) |
| ToString | Returns the value as a string. | ToString(<VALUE>) | ToString(123) |
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 5-row-4 6-row-4 7-row-4 8-row-4 9-row-4 10-row-4 11-row-4 12-row-4 13-row-4 14-row-4 15-row-4 16-row-4 17-row-4 18-row-4 19-row-4 20-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| AllNonNull2 | Takes two strings and checks if all of them are not null and not empty. | AllNonNull2(<STRING>, <STRING>) | AllNonNull2(“”, “string2”) |
| AllNonNull3 | Takes three strings and checks if all of them are not null and not empty | AllNonNull3(<STRING>, <STRING>, <STRING>) | AllNonNull3(“”, “one”, “three”) |
| Char | Takes an array of Unicode codepoints and returns the resulting string. | Char(<ARRAY>) | Char([65, 68, 79, 66, 69]) |
| Charindex | Finds the first occurrence of the specified substring within the main string. | Charindex(<STRING>, <SUBSTRING>) | Charindex (“bar@example.com”, “@”) |
| dataLength | Returns the number of bytes in the string. | dataLength(<STRING>) | dataLength(“My string”) |
| GetLine | Return the requested line of the provided string. | GetLine(<STRING>, <NUMBER>) | GetLine(multilinestring, 5) |
| IfEquals | Takes four strings and returns the third string if the first two strings are equal and returns the fourth string if the first two strings are not equal. | IfEquals(<STRING>, <STRING>, <STRING>, <STRING>) | IfEquals(“a”, “a”, “yes”, “no”) |
| IsMemoNull | Returns 1 if the string is null, otherwise it returns 0. | IsMemoNull(<STRING>) | IsMemoNull(“hello”) |
| JuxtWords | Takes two strings and combines them into a single string. Spaces between the strings are added if required. | JuxtWords(<STRING>, <STRING>) | JuxtWords(“Hello”, “World”) |
| JuxtWords3 | Takes three strings and combines them into a single string. Spaces between the strings are added if required. | JuxtWords3(<STRING>, <STRING>, <STRING>) | JuxtWords3(“Hello”, “New”, “World”) |
| Left | Takes a string and returns the leftmost characters as specified. | Left(<STRING>, <NUMBER>) | Left(“Substring”, 3) |
| Length | Returns the length of the string. | Length(<STRING>) | Length(“MyString”) |
| Line | Returns the specified numbered line from the string. | Line(<STRING>, <NUMBER>) | Line(multilinestring, 5) |
| Md5Digest | Converts the MD5-hashed string into its hexadecimal representation. | Md5Digest(<STRING>) | Md5Digest(“String”) |
| Replace | Takes a string and replaces all instances of the substring with a replacement substring. | Replace(<STRING>, <STRING>, <STRING>) | Replace(“Captain Steve”, “Captain”, “Engineer”) |
| Right | Takes a string and returns the rightmost characteres as specified. | Right(<STRING>, <NUMBER>) | Right (“Substring”, 3) |
| Sha256Digest | Converts the SHA256-hashed string into its hexadecimal representation. | Sha256Digest(<STRING>) | Sha256Digest(“string”) |
| Sha512Digest | Converts the SHA512-hashed string into its hexadecimal representation. | Sha512Digest(<STRING>) | Sha512Digest(“string”) |
| Smart | Returns the string with the first letter of each word capitalized. | Smart(<STRING>) | Smart(“hello world”) |
| ToString | Returns the value as a string. | ToString(<VALUE>) | ToString(123) |
Window
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| RowNum | Returns a sequence of rows based on the table partition and the sorting sequence. | RowNum(PartitionBy(<EXPRESSION>), OrderBy(<EXPRESSION>)) | RowNum(PartitionBy(division), OrderBy(time)) |
| PartitionBy | Separates the input rows into different partitions, based on the expression given. | PartitionBy(<EXPRESSION>) | PartitionBy(division) |
| OrderBy | Sorts the result of the partition. | OrderBy(<EXPRESSION>) | OrderBy(age) |
| Desc | Lets your OrderBy sort by descending order, rather than ascending order. | Desc(OrderBy(<EXPRESSION>)) | Desc(OrderBy(age)) |
| table 0-row-4 1-row-4 2-row-4 3-row-4 4-row-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Description | Syntax | Example |
| RowNum | Returns a sequence of rows based on the table partition and the sorting sequence. | RowNum(PartitionBy(<EXPRESSION>), OrderBy(<EXPRESSION>)) | RowNum(PartitionBy(division), OrderBy(time)) |
| PartitionBy | Separates the input rows into different partitions, based on the expression given. | PartitionBy(<EXPRESSION>) | PartitionBy(division) |
| OrderBy | Sorts the result of the partition. | OrderBy(<EXPRESSION>) | OrderBy(age) |
| Desc | Lets your OrderBy sort by descending order, rather than ascending order. | Desc(OrderBy(<EXPRESSION>)) | Desc(OrderBy(age)) |